What Causes Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke?
Possible Causes of Atrial Fibrillation Include1
High blood pressure
Heart attacks
Previous heart surgery
Coronary artery disease
Abnormal heart valves
Heart problems you're born with
Improper functioning of the heart's natural pacemaker
Chronic lung disease
Hyperthyroidism or other metabolic imbalances
Stress due to surgery, pneumonia, or other illnesses
Viral infections
Sleep apnea
Exposure to certain stimulants, including some medications, caffeine, tobacco, and alcohol
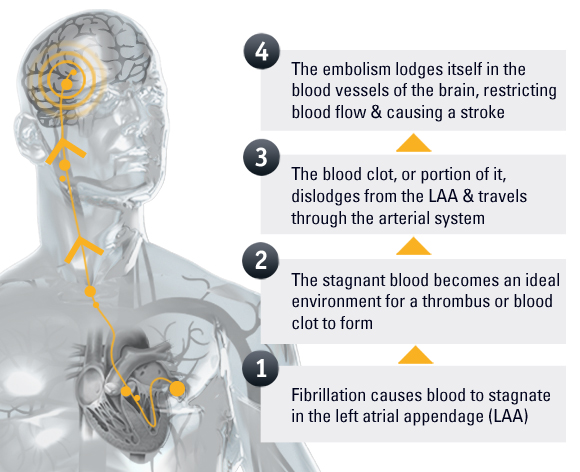
Atrial fibrillation can decrease the heart’s ability to pump by as much as 30 percent. As a result, blood pools in the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria. Since the blood isn’t pumped out of the heart normally, it’s easier for the blood cells to stick together and form clots in the left atrium, especially in an area called the left atrial appendage (LAA). The LAA is about the size of your thumb and looks like a small pouch on the top of your heart.
Blood clots can break loose from the LAA and travel to the brain, lungs, and other parts of the body, causing a stroke. In non-valvular AFib, the LAA is believed to be the source of most stroke-causing blood clots.2 But the good news is that there are a variety of treatments that can help reduce your risk of stroke.
Atrial fibrillation can decrease the heart’s ability to pump by as much as 30 percent. As a result, blood pools in the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria. Since the blood isn’t pumped out of the heart normally, it’s easier for the blood cells to stick together and form clots in the left atrium, especially in an area called the left atrial appendage (LAA). The LAA is about the size of your thumb and looks like a small pouch on the top of your heart.
Blood clots can break loose from the LAA and travel to the brain, lungs, and other parts of the body, causing a stroke. In non-valvular AFib, the LAA is believed to be the source of most stroke-causing blood clots.2 But the good news is that there are a variety of treatments that can help reduce your risk of stroke.
Anyone can have a stroke, regardless of age, race, or gender. But certain risk factors can increase your chance of having a stroke, including: