Alternative treatment to OAC
Getting to the Heart of the Problem
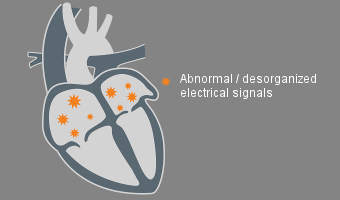
WHAT IS
ATRIAL FBRILLATION?
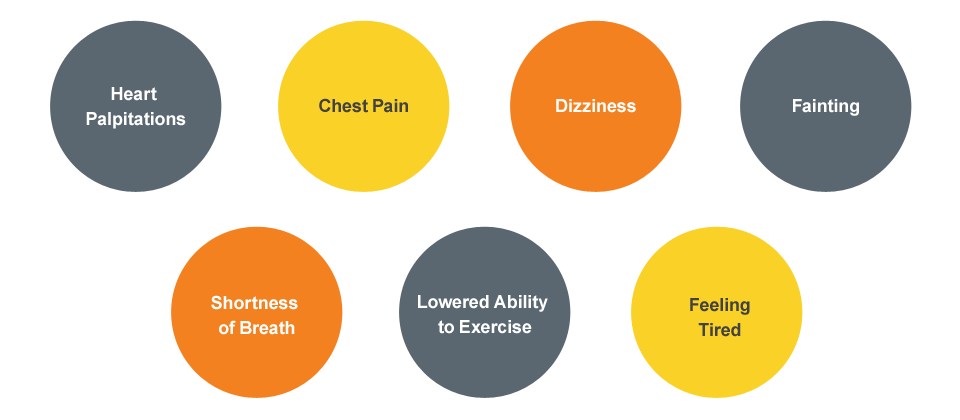
SYMPTOMS
AFIB
Those who do have symptoms may experience the following:
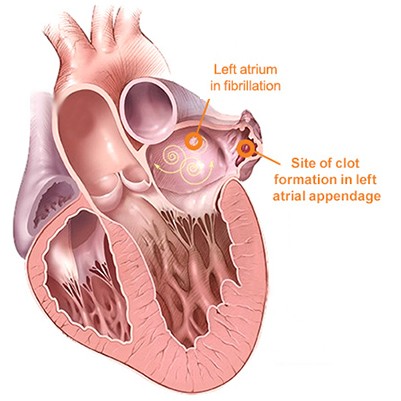
STROKE
- Sudden numbness, weakness, or paralysis of the face, arm, or leg (especially only on side of the body)
- Sudden confusion
- Sudden trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance, or lack of coordination
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
What Are My Treatment Options?
TREATMENTS TO REDUCE
AFIB STROKE RISK
To lower the risk of stroke, doctors may prescribe blood-thinning medications (anticoagulants) that help prevent clots from forming. These medications include warfarin (commonly called Coumadin®) and newer approved blood thinners.
Blood thinners are very effective in lowering the risk of stroke in people with AFib. Most patients can safely take these medications for years and even decades without serious side effects.
However, because anticoagulants help prevent clots by thinning the blood, they can also increase the risk of bleeding problems. Some bleeding events are minor and easily treated, like a cut taking longer to stop bleeding than normal. In other cases, bleeding can be serious and require hospitalization. Sometimes, the bleeding can be life-threatening or fatal, such as when bleeding in the brain causes a stroke.
For some patients, the risk of major bleeding is higher than for others. When prescribing blood thinners, doctors weigh the risk of a stroke against the risk of a serious bleeding problem. These risks vary depending on existing medical conditions, family history, lifestyle, and other factors.
In addition to clots traveling to the brain from the LAA, other factors can cause a stroke, including high blood pressure and narrowing of the blood vessels to the brain. The WATCHMAN Implant will not prevent these other causes of stroke.
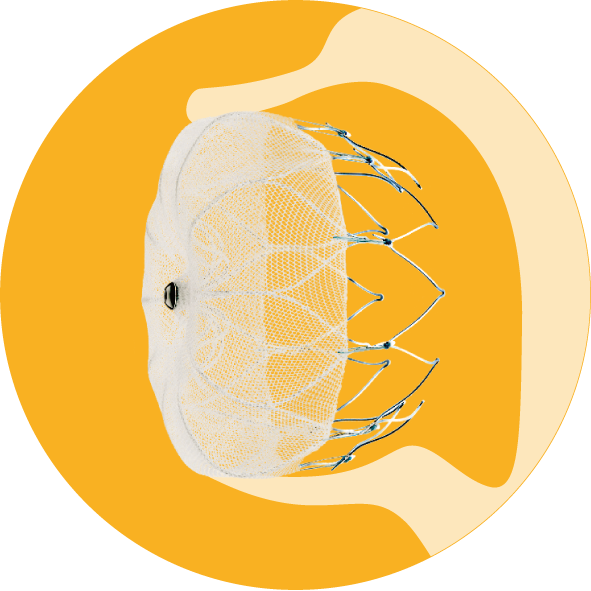
It’s also important to understand that, like blood thinners, the WATCHMAN Implant does not cure atrial fibrillation. However, it does offer a potentially life-changing treatment option that can free people with AFib from the burden of taking blood thinners long term.
How Does WATCHMAN LAAC Work?
Patient Testimonials
.
Resources
Get help discussing your treatment options with your doctor with our Doctor Discussion Guide

Find a Doctor