Patient Selection

S-ICD is Guideline Recommended
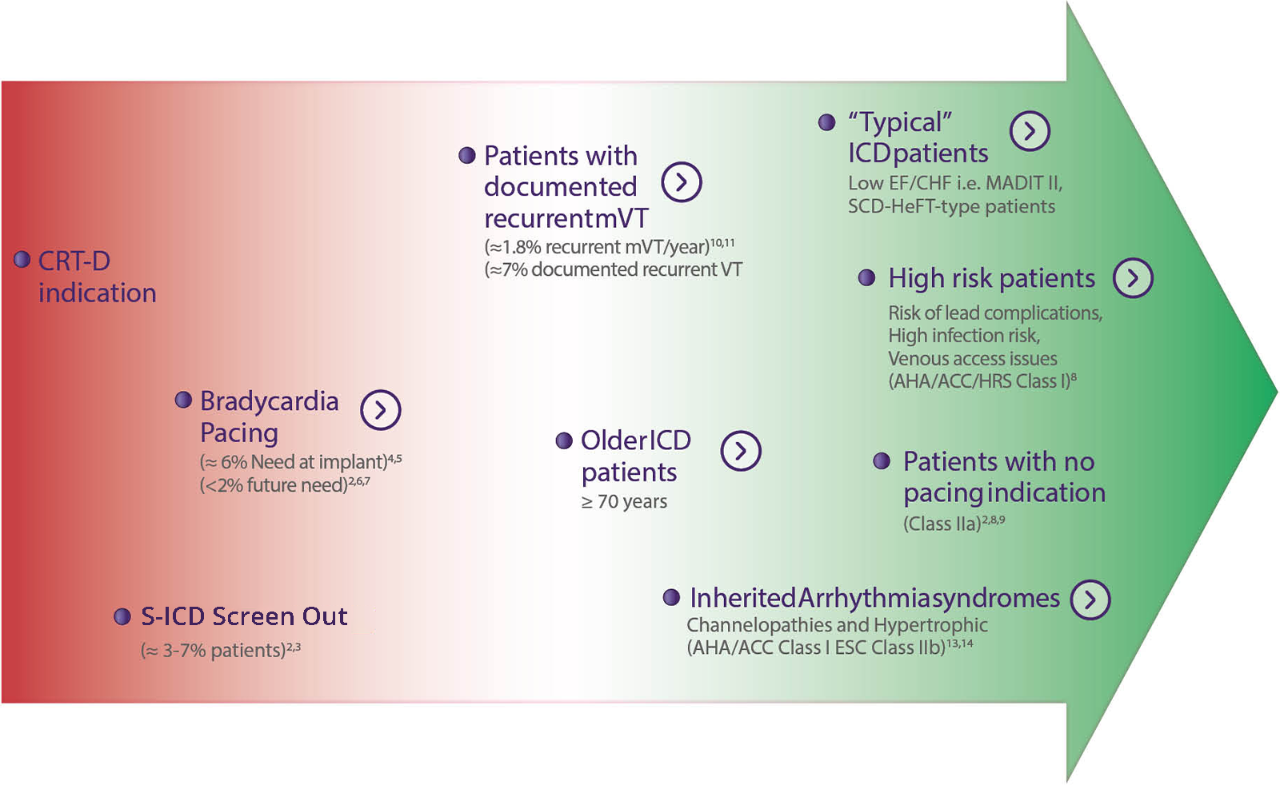
Clinical Data Supports S-ICD for a Broad Group of Patients
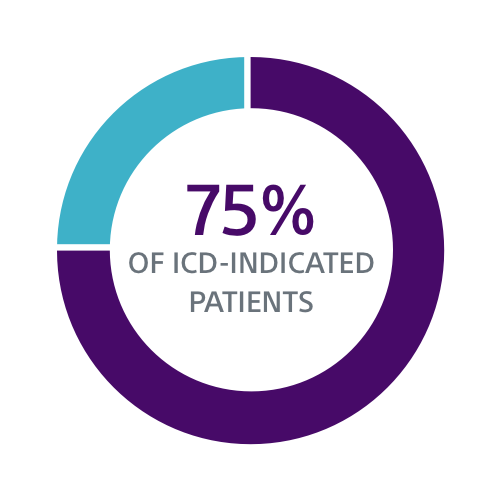
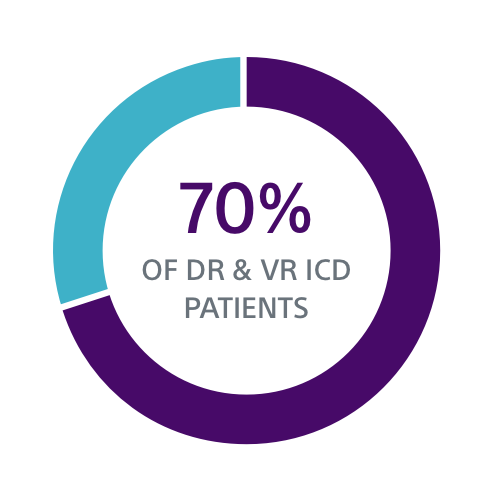
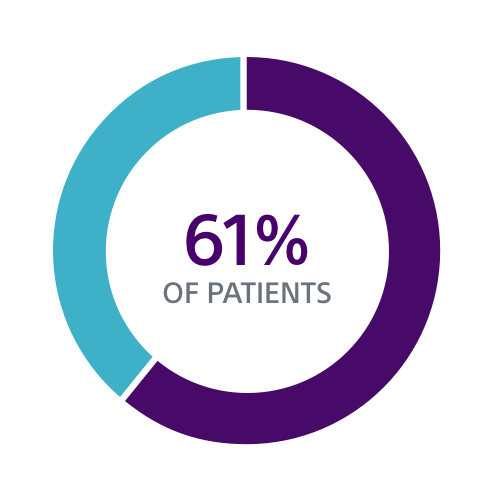
Both the PRAETORIAN and UNTOUCHED studies confirm S-ICD should be considered the first choice for all ICD-indicated patients without a pacing indication.
PRAETORIAN2
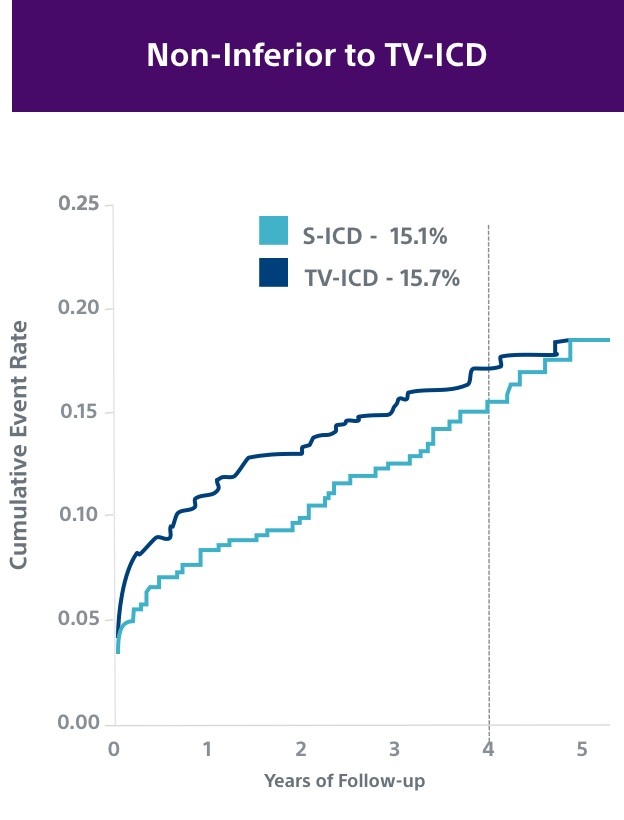
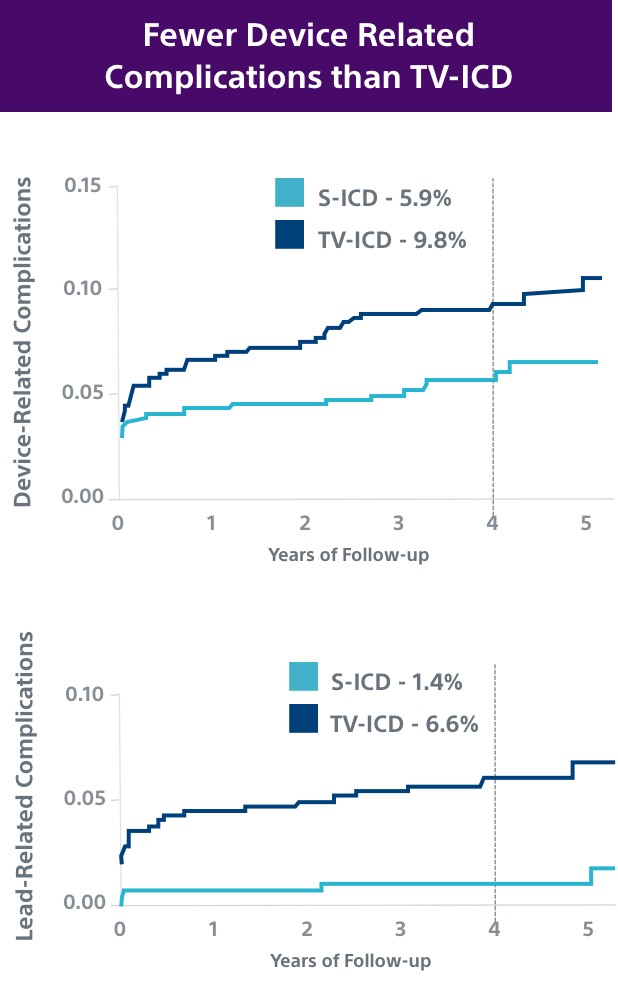
This investigator-sponsored trial demonstrated S-ICD had comparable performance to TV-ICD, despite including primarily older S-ICD devices and implant techniques. According to the PRAETORIAN study, S-ICD:
- Had significantly fewer lead-related complications (1.4% vs. 6.6%, P=0.001)
- Demonstrated fewer serious infections requiring extraction (8 TV-ICD vs. 4 S-ICD)
- Showed a trend in fewer overall complications (5.9% vs. 9.8%, P=0.11); likely to be significantly lower at 8 years in PRAETORIAN XL
UNTOUCHED6
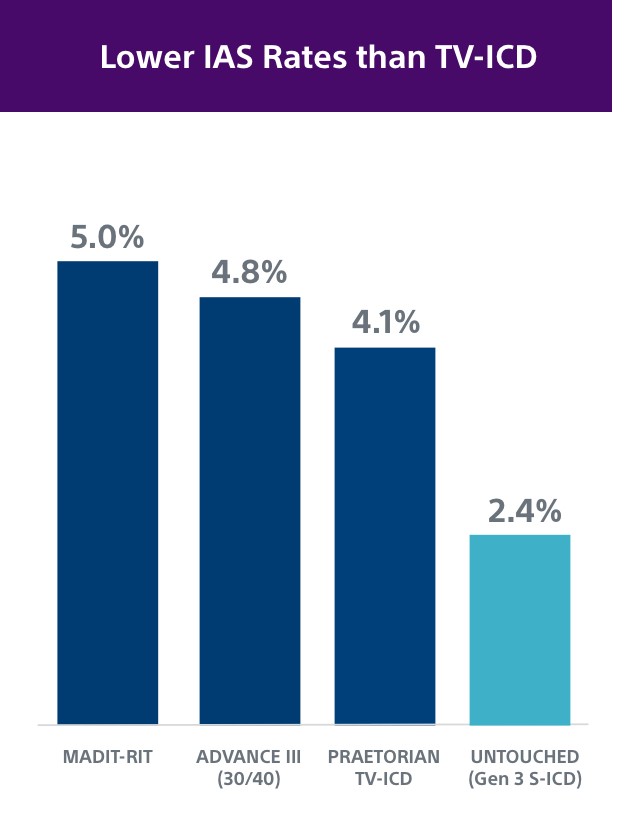
The UNTOUCHED study demonstrated patients with EMBLEM™ MRI S-ICD with SMART Pass had a 2.4% rate of inappropriate shocks at 1 year, which is as low or lower than TV-ICD devices.2,18,21,22
As S-ICD Technology Evolves, So Does the Clinical Data
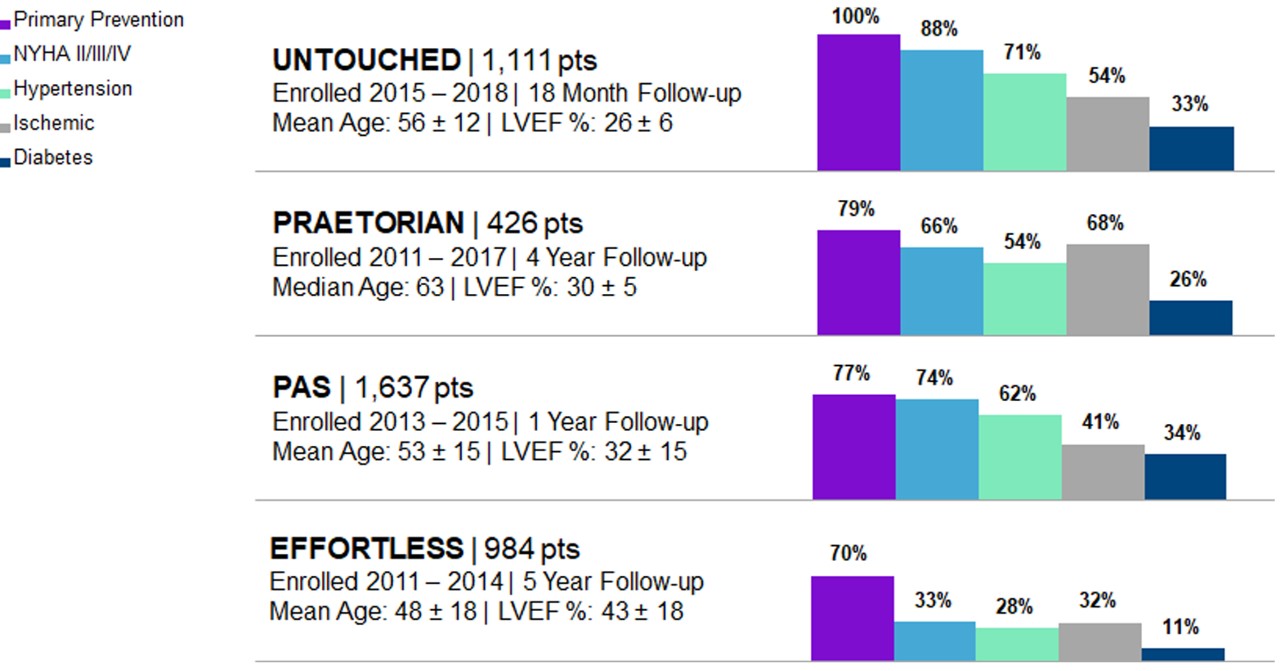
Early S-ICD trials typically had younger patients with less advanced heart disease and “niche” indications, including channelopathies, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease or previous ICD indication. However, both the PRAETORIAN and UNTOUCHED studies included older and sicker patients. In fact, UNTOUCHED included the most traditional cohort of patients (primary prevention, LVEF ≤ 35%) and showed the S-ICD has lower inappropriate shock (IAS) rates than TV-ICDs.
Patient Comorbidities and S-ICD
It’s important to consider patient comorbidities and other risk factors for complications when determining whether a TV-ICD is required or if a patient should be offered both S-ICD and TV-ICD when taking a shared decision-making approach to the treatment decision.
Patient Comorbidities |
S-ICD |
TV-ICD Required2,8 |
TV-ICD Considered2,8 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluating Need for Brady Pacing7,23-24 | Brady pacing indication at implant |
|
|
|
No current pacing indication, but has 1 or more of the following:
|
|
|
||
| No pacing indication at implant and age < 80 |
|
|
|
|
| High Risk for TV Lead Failure25 | Life expectancy > 8 years |
|
|
|
| High Risk for Infection15 | H/O device infection |
|
|
|
| Prosthetic heart valve |
|
|
||
| On dialysis or renal insufficiency |
|
|
||
| Diabetes |
|
|
||
Other risk factors:
|
|
|
||
| High or Low Risk for ATP26-27 | Ischemic or non-ischemic heart failure or ICD-indicated patient with NO history of recurrent sustained monomorphic VT |
|
||
ICD-indicated patient WITH a history of recurrent sustained monomorphic VT amenable to ATP therapy |
|

Education & Training
Why S-ICD?
See how S-ICD helps protect patients at risk for sudden cardiac death while also eliminating the risk of TV-ICD lead complications.