About MANAGE-HF1,2
Overview
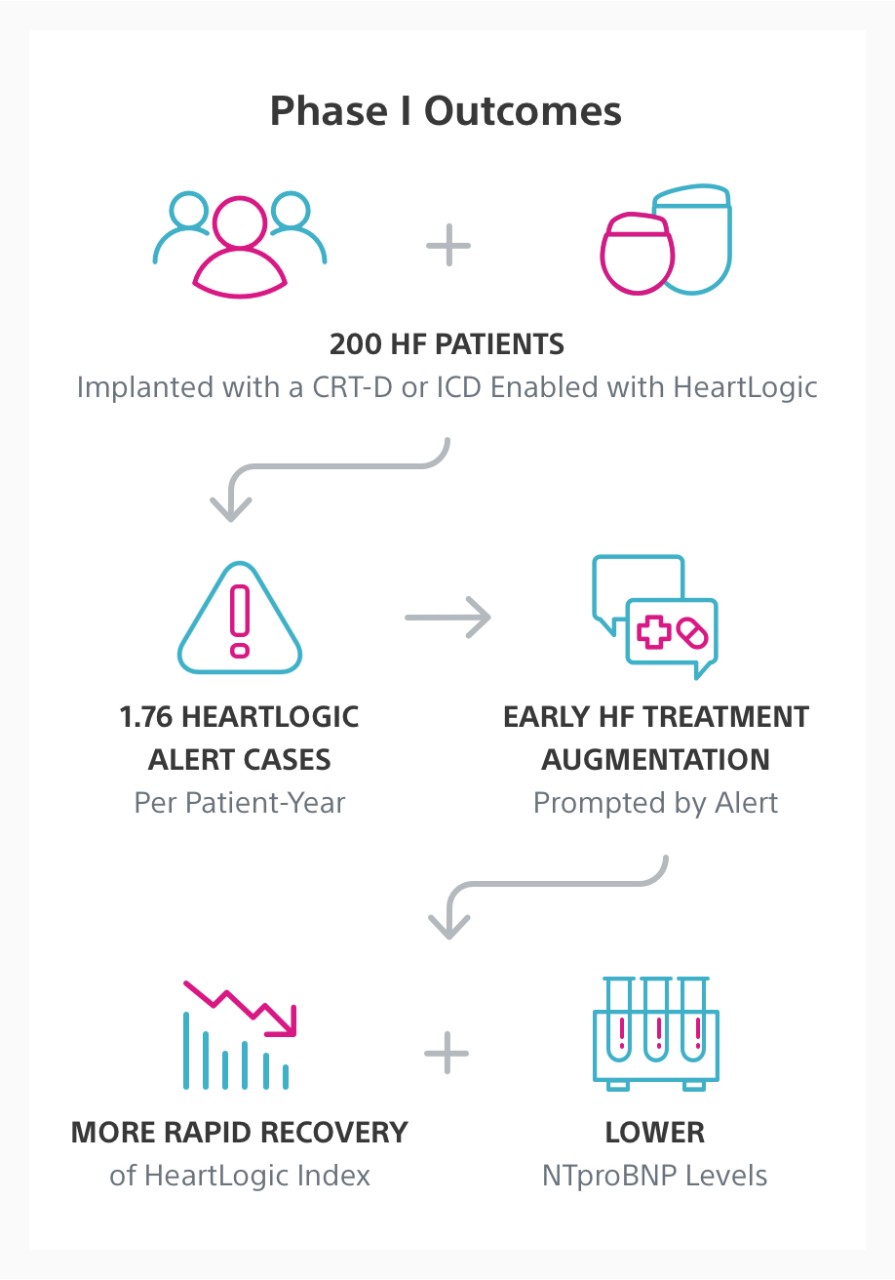
The MANAGE-HF study is a multi-center, global, prospective, open-label, multi-phase trial. Phase I enrolled 200 patients implanted with a CRT-D or ICD enabled with the HeartLogic™ Heart Failure Diagnostic.
Goals
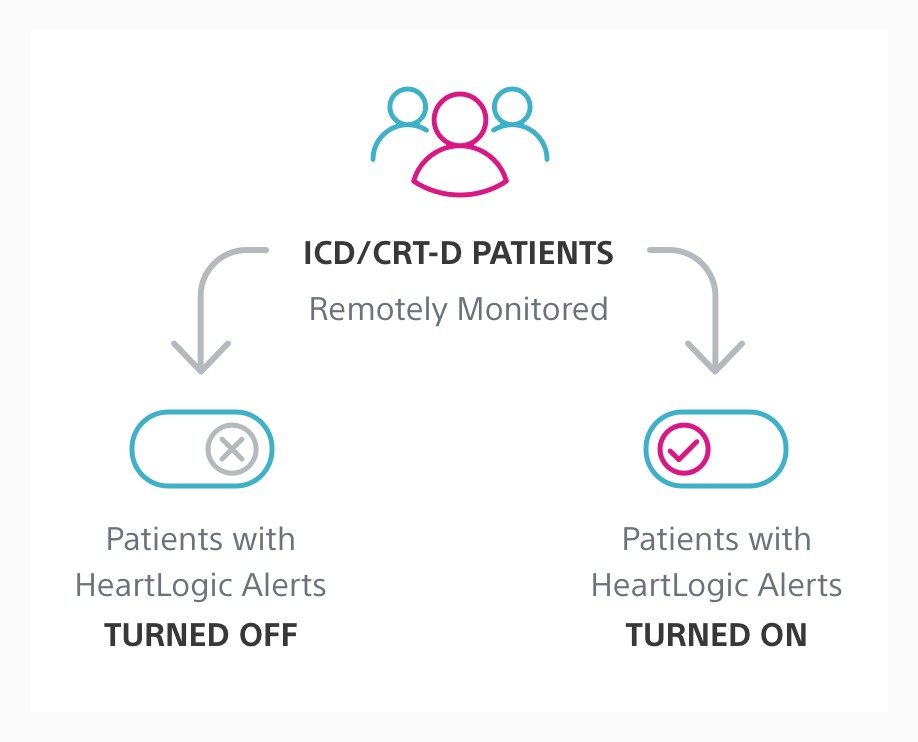
The goal of Phase I was to evaluate and optimise the integration of HeartLogic into clinical practice for the treatment of heart failure (HF). Phase II of the MANAGE-HF study will evaluate the efficacy of augmented HF treatment in remotely monitored patients with HeartLogic alerts turned on compared to patients with alerts turned off.
Conclusions
In Phase I, HeartLogic was integrated into clinical care safely and early treatment augmentation was associated with more rapid recovery of the HeartLogic index compared to patients with no change in treatment following an alert.
Safe Integration into Clinical Practice
Phase I of the MANAGE-HF study demonstrated the HeartLogic multisensor algorithm was safely integrated into clinical practice. In 333 patient-years of follow-up:2
- 74% of alert cases prompted augmentation of HF medications relative to pre-alert dose
- HF medications were augmented relative to pre-alert dose within 7 days of 54% of weekly alerts
- 89% of HF medications augmented within seven days of weekly alerts were diuretics
- Only five serious adverse events* (SAEs) in relation to alert-prompted medication changes were reported, which translates to 0.015 SAEs per patient-year
The low number of SAEs in the study suggests that alert-prompted medication changes did not result in overly aggressive heart failure management practices.
*SAEs above were classified as abnormal laboratory values, renal insufficiency/failure, dizziness, or syncope in response to an alert-prompted medication change.2
Early HF Treatment Augmentation
Early decongestive treatment in response to an alert was associated with more rapid recovery of the HeartLogic index compared to patients with no change in treatment following an alert. In addition, HeartLogic was associated with lower hospitalisation rates and N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) levels.
MANAGE-HF: Phase I Study Highlights
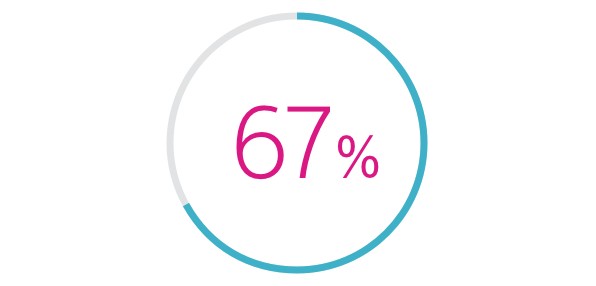
- HeartLogic was associated with a 67% reduction in heart failure hospitalisations compared to pre-study, 12-month HF hospitalisation rate
- NTproBNP levels significantly decreased from median 1316 pg/mL at baseline to 743 pg/mL at 12 months (p<0.001)
- 1.76 alert case/patient-year shown in MANAGE-HF Phase I was consistent with expectations based on alert case rate previously reported in MultiSENSE3
Phase II: Enrolling Early 2022
Sign up for periodic emails and receive a HeartLogic fact sheet to share with your patients’ care teams.
Explore the data showing that HeartLogic provides a sensitive and timely predictor of impending HF events.3
See how HeartLogic consistently detected HF events in real-world analyses of nearly 500 patients in four studies.