Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
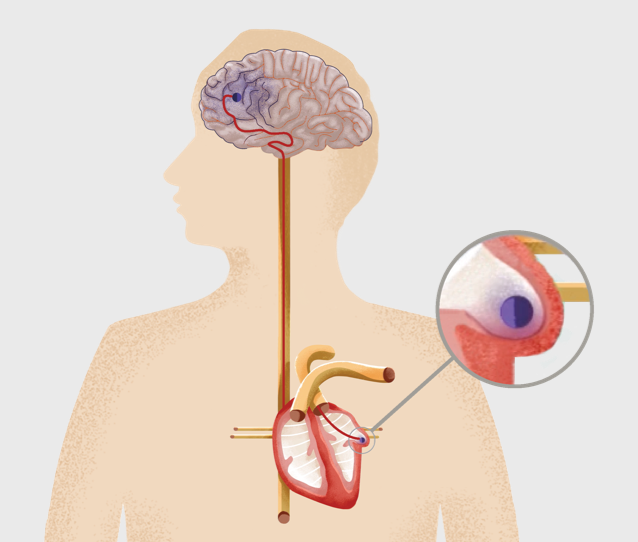
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)* is a heart condition in which the upper chambers of your heart quiver. This condition can cause blood clots to form in an area of your heart called the left atrial appendage (LAA). If a blood clot forms here, it can travel through an artery to the brain and cause a stroke.
People with AFib have a five‑times greater risk for stroke than people with normal heart rhythms.1
Managing AFib and Stroke Risk
The study will research the safety and effectiveness of the WATCHMAN FLX device compared to treatment with NOAC therapy to determine its effectiveness in stroke risk reduction for patients with AFib not caused by a heart valve problem.
Understanding Left Atrial Appendage Closure Surgery with the WATCHMAN Implant

The Implant Procedure
Here's what happens during the procedure.
 |
Step 1To implant the device, your doctor inserts a narrow tube into a vein in your upper leg. |
 |
Step 2Your doctor guides the device through the tube, into your left atrial appendage (LAA). |
 |
Step 3The procedure is typically done under general anesthesia and takes under an hour. People usually stay in the hospital overnight and go home the next day. |
 |
Step 4After the procedure, you will be on blood thinning medication, as prescribed by your study doctor. |
 |
Step 5Imaging of your heart will be performed 4 months after your procedure to see how well the heart tissue has grown over the implant. |
Why CHAMPION-AF?


Talk to Your Doctor
For more information, or to find out if you're an appropriate candidate for the CHAMPION-AF clinical trial, fill out and print the simple trial discussion guide below, and bring it to a scheduled appointment with your heart doctor.
* All mentions of 'AFib' or 'Atrial Fibrillation' specifically indicate atrial fibrillation, not caused by a heart valve problem.
1. Holmes D. Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke Management: Present and Future. Semin Neurol 2010, 30:528-536.
2. WatchUsNow.com. The Harris Poll online survey. Boston Scientific. SH-574213-AA.
https://www.watchusnow.com/?page=d75be9d4-ba36-456c-a72d-dc3df07892da. Accessed March 28, 2019.
Please talk to your physician about any additional risks related to the CHAMPION-AF trial.
Important Safety Information
The WATCHMAN and WATCHMAN FLX Devices are permanent implants designed to close the left atrial appendage in the heart in an effort to reduce the risk of stroke.
With all medical procedures there are risks associated with the implant procedure and the use of the device. The risks include but are not limited to accidental heart puncture, air embolism, allergic reaction, anemia, anesthesia risks, arrhythmias, AV (Arteriovenous) fistula, bleeding or throat pain from the TEE (Trans Esophageal Echo) probe, blood clot or air bubbles in the lungs or other organs, bruising at the catheter insertion site, clot formation on the device, cranial bleed, excessive bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding, groin puncture bleed, hypotension, infection/pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, pulmonary vein obstruction, renal failure, stroke, thrombosis and transient ischemic attack. In rare cases death can occur.
Be
sure to talk with your doctor so that you thoroughly understand all of
the risks and benefits associated with the implantation of the device.