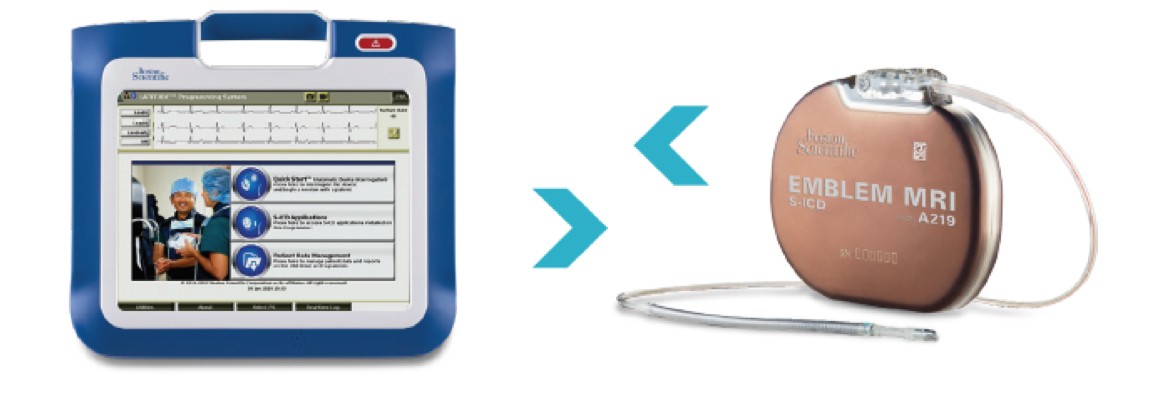
EMBLEM™ MRI S-ICD System
Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillator
AST 2.0 Now Available through the LATITUDE™ Programming System, Model 3300
S-ICD device performance.1

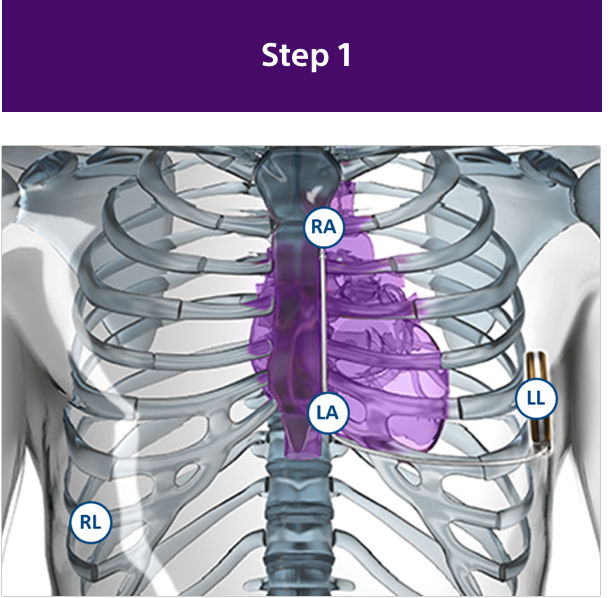
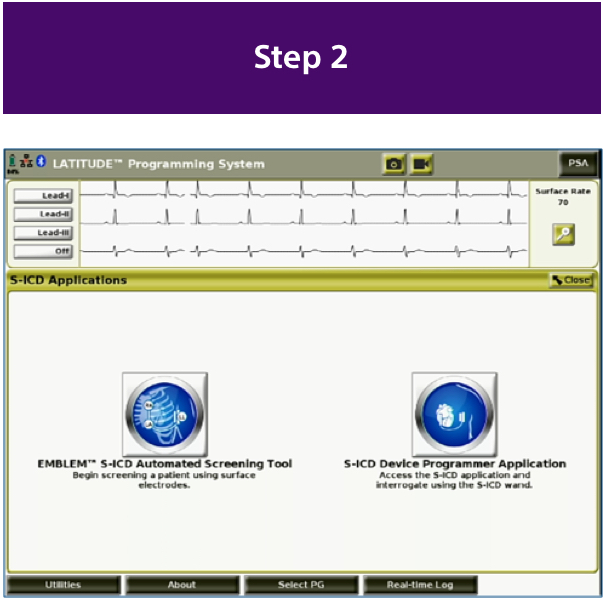
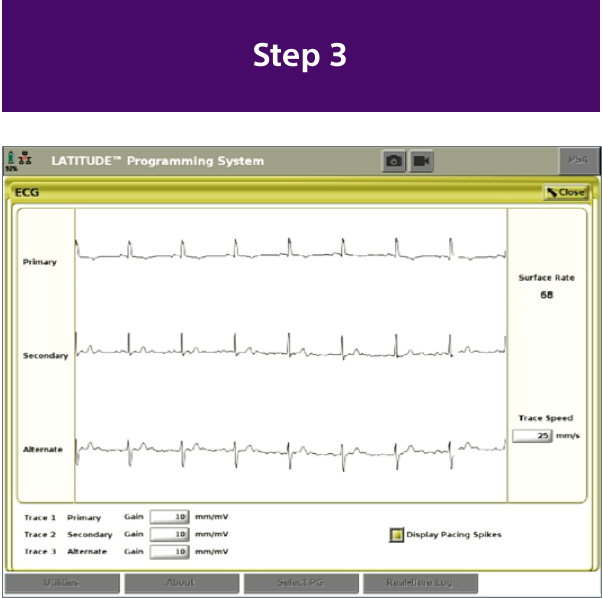
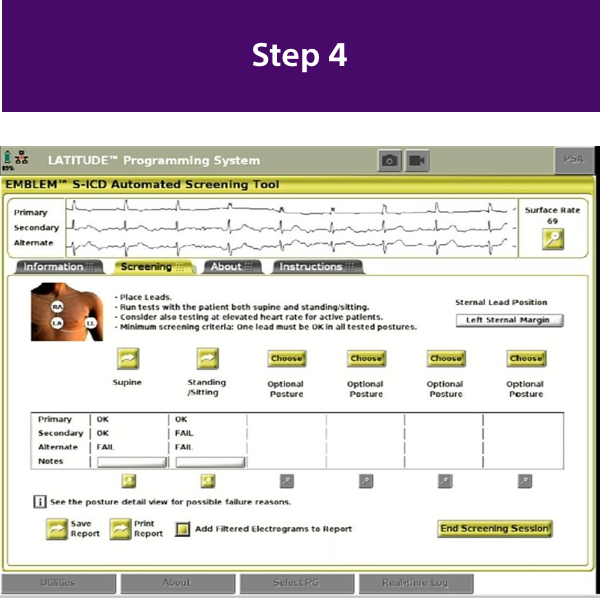
How to Do a Successful Screening
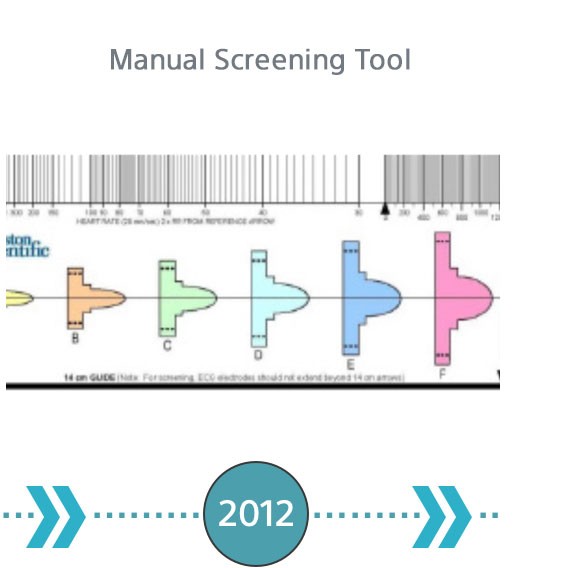
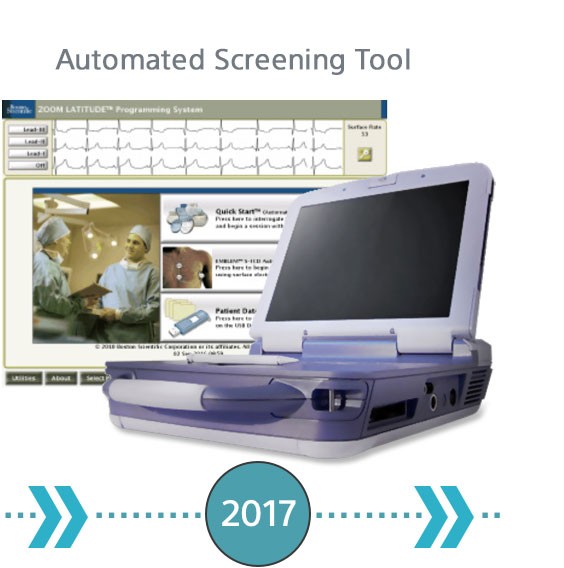
The Evolution of S-ICD Screening
Which Patients Should Be Screened for an S-ICD?
All ICD-indicated patients without a pacing need should be considered for an S-ICD.
Patient Comorbidities |
S-ICD |
TV-ICD Required3,4 |
TV-ICD Considered3,4 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluating Need for Brady Pacing5-7 | Brady pacing indication at implant |
|
X |
|
No current pacing indication, but has 1 or more of the following:
|
|
X |
||
| No pacing indication at implant and age < 80 | X |
|
|
|
| High Risk for TV Lead Failure8 | Life expectancy > 8 years |
X |
|
|
| High Risk for Infection9 | H/O device infection | X |
|
|
| Prosthetic heart valve | X |
|
||
| On dialysis or renal insufficiency | X |
|
||
| Diabetes | X |
|
||
Other risk factors:
|
X |
|
||
| High or Low Risk for ATP10,11 | Ischemic or non-ischemic heart failure or ICD-indicated patient with NO history of recurrent sustained monomorphic VT |
X |
||
ICD-indicated patient WITH a history of recurrent sustained monomorphic VT amenable to ATP therapy |
X |

Training & Education

Explore continuing education courses, best practices modules and other training and
resources for S-ICD.
Why S-ICD?
See how S-ICD helps protect patients at risk for sudden cardiac death
while also eliminating the risk of TV-ICD lead complications.