HeartLogic Clinical Data
Explore the clinical data and real-world evidence showing how HeartLogic Heart Failure Diagnostic changes the future of electrophysiology and allows you to do things you couldn’t do before.
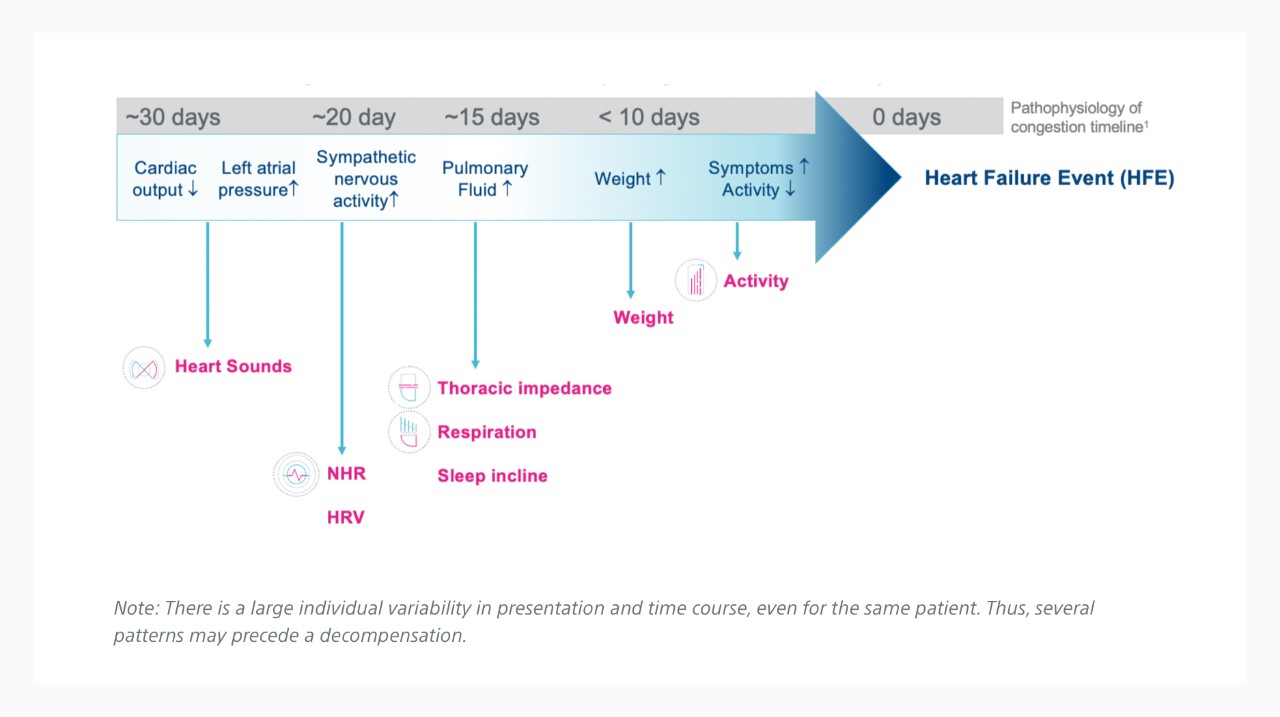
Time Course of HF Decompensation1
Emulating Clinical Assessment via Physiologic Sensor Monitoring
Electrophysiology Insights
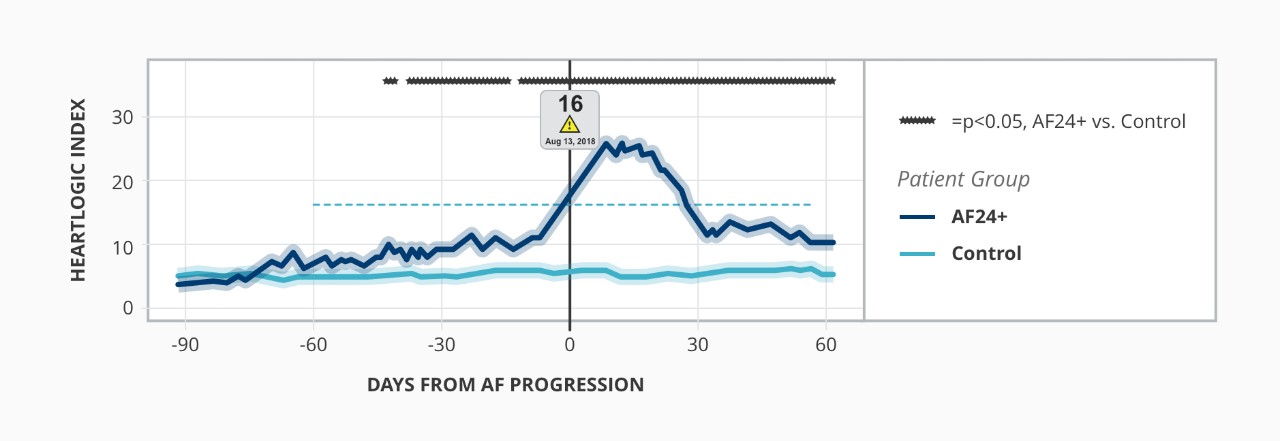
Relationship Between Atrial Fibrillation and HeartLogic Index2
MANAGE-HF Study5
MultiSENSE Study Results7
Real-World Evidence
Real-World Results Compared to Validation Data Set
| MultiSENSE7 (Validation Data Set) |
Capucci et al.2 (ESC HF 2019) |
Santini et al.8 (Clin Card 2020) |
RE-HEART Phase I9 (ESC HF 2020) |
RE-HEART Phase II10 (ESC HF 2020) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
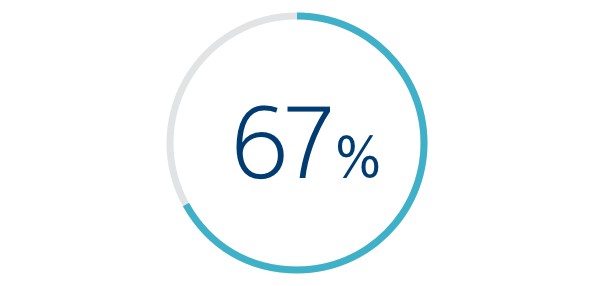
| SENSITIVITY | 70% | 100%* | 69%* | N/A | N/A |
| UNEXPLAINED ALERT RATE | 1.47 | 0.41 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
Highlights from Real-World Studies
Physician Perspectives

HeartLogic™ Data and Integration into Clinical Practice: HFSA 2021
Watch Dr. Marat Fudim, Dr. Andrew Sauer and Dr. Larry Allen discuss HeartLogic, review case studies and highlight results from the MANAGE-HF Clinical Study.

Integrated Heart Failure Patient Management EP and HF Perspective
Listen as three members of the Duke University Medical Center team – Dr. Marat Fudim, Dr. Camille Frazier-Mills and Dr. Adrian Hernandez – share their experience collaborating to implement HeartLogic™ in clinical care and demonstrate through case studies the value of integrated care.

HeartLogic Clinical Compendium
Review a compilation of relevant publication references that form the clinical foundation of the HeartLogic Heart Failure Diagnostic, organized by sensor trend/topic area and relevance.


Stay Up to Date
Sign up for periodic emails and receive a HeartLogic fact sheet to share with your patients’ care teams.

Products
Your extraordinary talent. Our extraordinary technology. Explore the Boston Scientific CRT-Ds and ICDs that feature HeartLogic.
LATITUDE NXT™ Remote Patient Management System: Indications, Safety and Warnings
Resonate™ ICD: Indications, Safety and Warnings
Resonate™ CRT-D: Indications, Safety and Warnings
References
1. Adamson PB. Pathophysiology of the transition from chronic compensated and acute decompensated heart failure: new insights from continuous monitoring devices. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2009 Dec;6(4):287-92. doi: 10.1007/s11897-009-0039-z.
2. Capucci A, Healey JS. Temporal association of atrial fibrillation with device-based heart failure status in patients with CRT. Oral presentation and LBCT presented at: EHRA Congress; March 2019, Lisbon, Portugal.
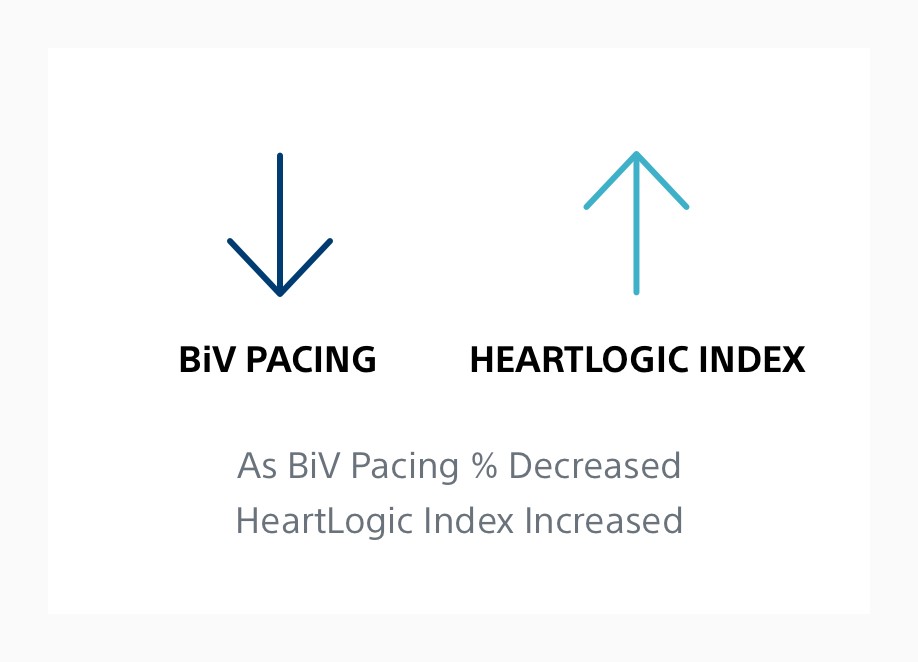
3. Varma N, Cao M, Schloss EJ, Ahmed R, Stolen C, Boehmer JP. Progressive worsening in device base failure sensors measurements are associated with sub-optimal BiV pacing percentages in CRT-D patients. J Heart Fail. 2019;21(Suppl. S1):370. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1488
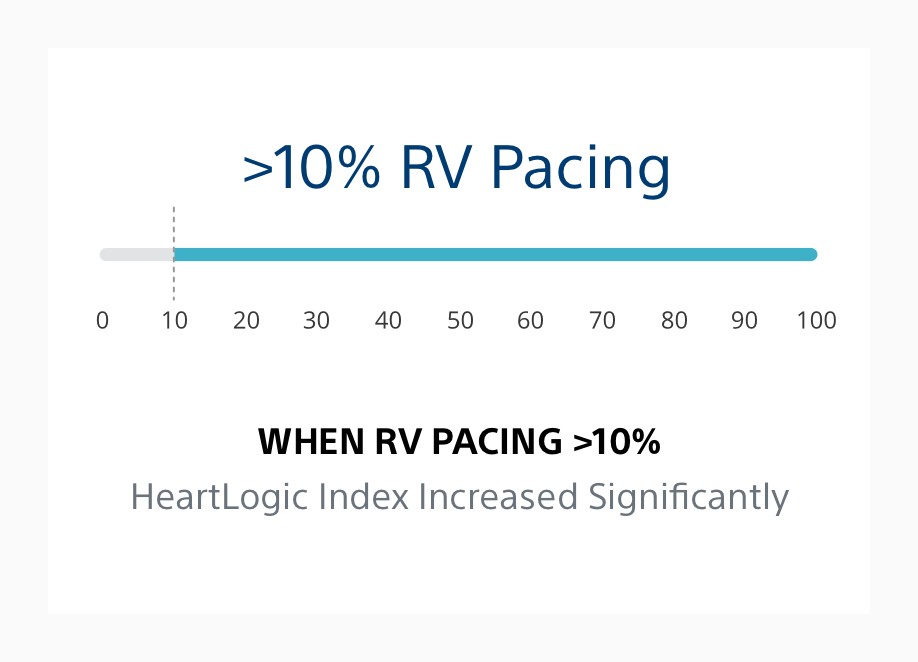
4. Varma N, Stein KM, Thakur PH, Jones PW, Ahmed R, J Boehmer J. Multiparametric analysis of device based physiological sensors may identify ICD patients reacting adversely to right ventricular pacing [abstract]. Heart Rhythm. 2019;16(5):S58-S59.
5. Multiple Cardiac Sensors for the Management of Heart Failure (MANAGE-HF).
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03237858
6. Hernandez AF, Albert N, Allen L, et al. Multiple cardiac sensors for management of heart failure (MANAGE-HF) Phase I results. Abstract presented at: European Society of Heart Failure 2021 World Congress on Acute Heart Failure: June 29-July 1, 2021. Virtual.
7. Boehmer JP, Hariharan R, Devecchi FG, et al. A multisensor algorithm predicts heart failure events in patients with implanted devices: results from the MultiSENSE study. JACC Heart Fail. 2017 Mar;5(3):216-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2016.12.011.
8. Santini L, D’Onofrio A, Russo AD, et al. Prospective evaluation of the multisensor HeartLogic algorithm for heart failure monitoring. Clin Card. 2020;43(7):691-697. doi: 10.1002/clc.23366
9. De Juan Baguda J, Gavira Gomex JJ, Pachó Iglesias M, et al. Preliminary results of the Spanish multicentric HeartLogic (RE-HEART) registry: a blinded analysis. Abstract presented virtually at: ESC-HFA Congress 2020.
10. De Juan Baguda J, Gavira Gomex JJ, Pachó Iglesias M, et al. Preliminary results of the Spanish multicentric HeartLogic (RE-HEART) registry: adoption of an alert-based heart failure management approach. Abstract presented virtually at: ESC-HFA Congress 2020.
*The HeartLogic Index and Alert were validated using data from the MultiSENSE study; however, HeartLogic’s impact on clinical outcome has not been established. Establishment of the impact will require a post market trial designed specifically to study clinical outcomes directly related to the use of this feature.