Eficácia clínica da DBS para a doença de Parkinson
Principais recursos
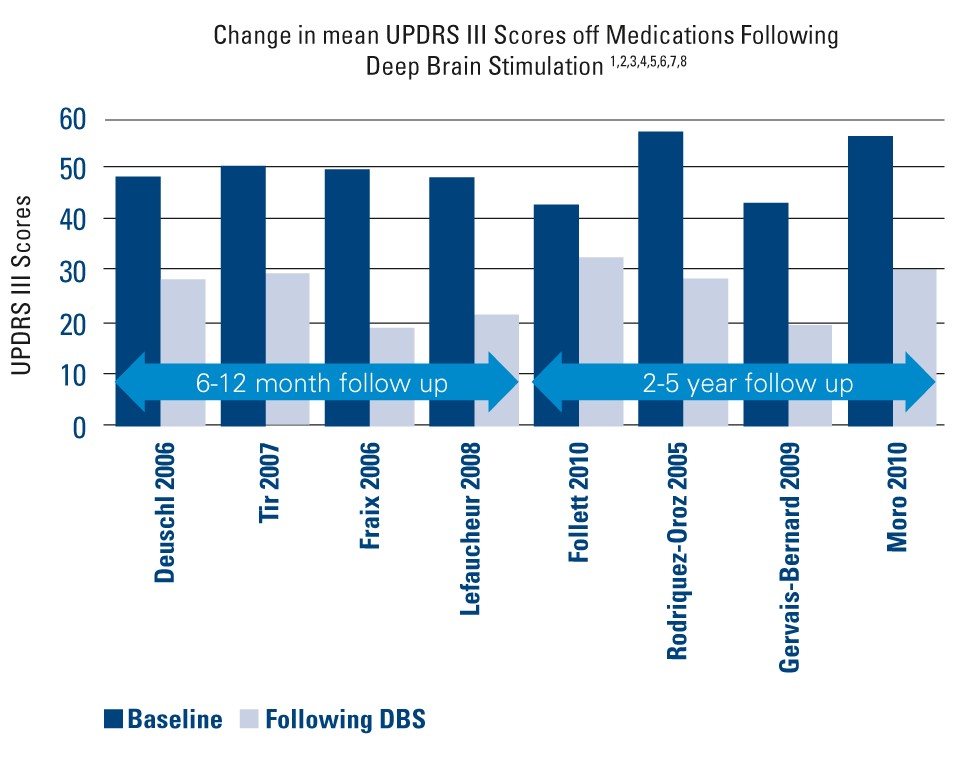
Autor | Desenho do estudo | Tamanho da amostra | Acompanhamento | Mudança nas pontuações médias de UPDRS III | % de melhoria em UPDRS III & Pontuações PDQ-39 |
| Deuschl 2006¹ | Estudo randomizado em pares | 78 | 6 meses | • Linha de base: 48 ± 12,3 • Pós-DBS: 28,3 ± 14 | • Melhoria de 41% em UPDRS III • Melhoria de 25% em PDQ-39 |
| Tir 2007² | Estudo prospectivo, unicêntrico | 103 | 12 meses | • Linha de base: 50 ± 16 • Pós-DBS: 29 ± 11,5 | • Melhoria de 42% em UPDRS III |
| Fraix 2006³ | Prospectivo e multicêntrico | 95 | 12 meses | • Linha de base: 49,2 ± 16,4 • Pós-DBS: 19,4 ± 11,5 | • Melhoria de 57% em UPDRS III |
| Lefaucheur 2008⁴ | Estudo unicêntrico | 54 | 12 meses | • Linha de base: 48,2 ± 16,1 • Pós-DBS: 21,4 ± 8,2 | • Melhoria de 56% em UPDRS III |
| Follett 2010⁵ | Multicêntrico, randomizado, cego | 299 | 24 meses | STN • Linha de base: 43 ± 15 • Pós-DBS: 32,1 ± 15,6 GPi • Linha de base: 41,8 ± 13,1 • Pós-DBS: 30 ± 14,2 | • Melhoria de 25,3% em UPDRS III • Melhoria em 6 de 8 subescalas |
| Rodriquez-Oroz 2005⁶ | Estudo multicêntrico | 69 | 3-4 anos | STN • Linha de base: 56,7 ± 15,7 • Pós-DBS: 28,6 ± 15,7 GPi • Linha de base: 51,7 ± 13,6 • Pós-DBS: 31,7 ± 12,8 | • Melhoria de 50% em UPDRS III • com STN e melhoria de 39% improvement • com GPi em 3 a 4 anos |
| Gervais-Bernard 2009⁷ | Prospectivo, unicêntrico | 23 | 5 anos | • Linha de base: 43,11 ± 14,04 • Pós-DBS: 19,52 ± 7,17 | • Melhoria de 55% em UPDRS III |
| Moro 2010⁸ | Estudo multicêntrico, não randomizado, prospectivo, cego | 51 | 5 a 6 anos | STN • Linha de base: 56 ± 2,7 • Pós-DBS: 30,1 ± 2,5 GPi • Linha de base: 52,2 ± 3,5 • Pós-DBS: 32,6 ± 4,6 | • 45,4 (STN) para melhoria de 20% (GPi) em UPDRS III |
• |
• |
• |
Referências
Referências
1. Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C et al. A Randomized Trial of Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. N Engl J Med 2006;355:896-908.
2. Tir M, Exhaustive, one-year follow-up of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in a large, single-center cohort of Parkinson’s patients, Neurosurgery 61:297–305, 2007.
3. Fraix V, Houeto JL, Lagrange C et al. Clinical and economic results of bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2006;77:443–449.
4. Lafaucheur JP, Gurruchaga JM, Pollin B et al. Outcome of Bilateral Subthalamic Nucleus Stimulation in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: Correlation with Intra-Operative Multi-Unit Recordings but Not with the Type of Anaesthesia. Eur Neurol 2008;60:186–199.
5. Follett KA, Weaver FM, Stern M et al. Pallidal versus Subthalamic Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. N Engl J Med 2010;362:2077-91.
6. Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Bilateral deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a multicentre study with 4 years follow-up, Brain (2005), 128, 2240–2249.
7. Gervais-Bernard H, Xie-Brustolin J, Mertens P et al, Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation in advanced Parkinson’s disease: Five year follow-up. J Neurol (2009) 256:225–233.
8. Moro E, Lozano A, Pollak P et al. Long-Term Results of a Multicenter Study on Subthalamic and Pallidal Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease. Movement Disorders
.