ULTRA ICE™️ PLUS
Ultrasound Imaging Catheter
ULTRA ICE™ PLUS Ultrasound Imaging Catheter for Intracardiac Imaging
ICE provides the combination of real-time imaging and soft tissue visualization that cannot be duplicated by fluoroscopy, pre-operative imaging (CT or MR), or electroanatomic mapping. Not only can you identify anatomical structures, you can visualize where devices are relative to those structures.
Key Resources
Explore
Product Details
ULTRA ICE PLUS Catheter
The Boston Scientific ULTRA ICE PLUS catheter is designed to provide precise, real-time visualization of both intracardiac anatomy and devices positioned within the heart. Not only does it help you in identifying anatomical structures, it also helps you in visualizing where your devices are relative to those structures.
Device Illustration
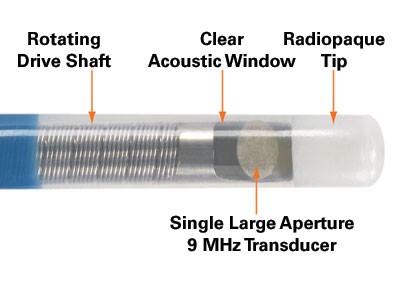
Unique Vision: 360° Views and Detailed Near-Field Resolution
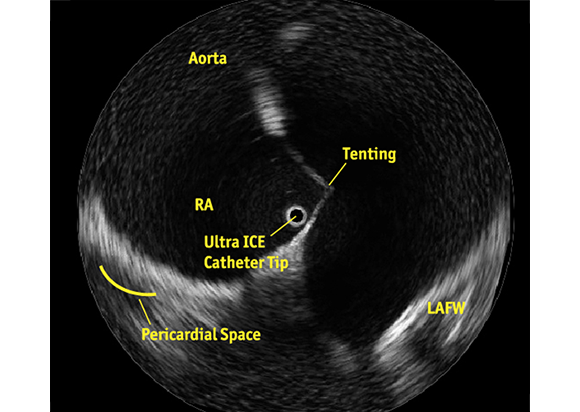
The ULTRA ICE PLUS Catheter generates a cross-sectional and panoramic 360° image perpendicular to the catheter, with the tip as a central reference point. This allows the user to visualize structures (such as the fossa) directly adjacent to the catheter tip and still see a detailed cross-section of the entire septum.
Image Comparison
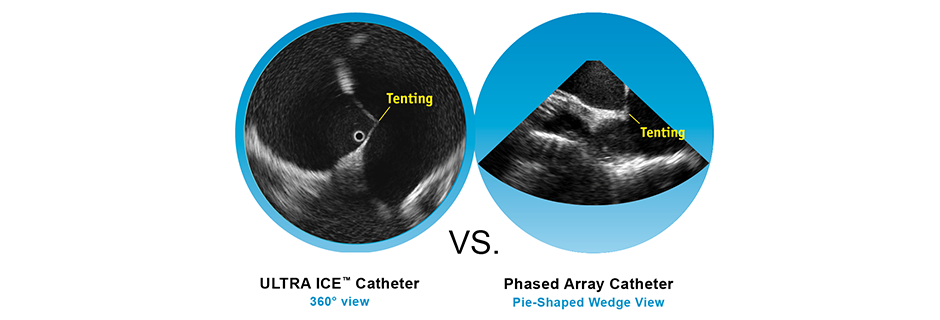
Benefit of Use
The ULTRA ICE PLUS catheter is indicated for enhanced visualization of cardiac structures and is designed to optimize performance when imaging by enabling users to position the catheter directly adjacent to areas of interest, like the proximal coronary sinus, fossa ovalis, or pulmonary veins. Its 360 degree, forward looking visualization field provides greater near-field resolution than phased array catheters, without the need to manually move the catheter away from a target area to adjust focal distance.
Know Where You Are
See What You Want to Avoid
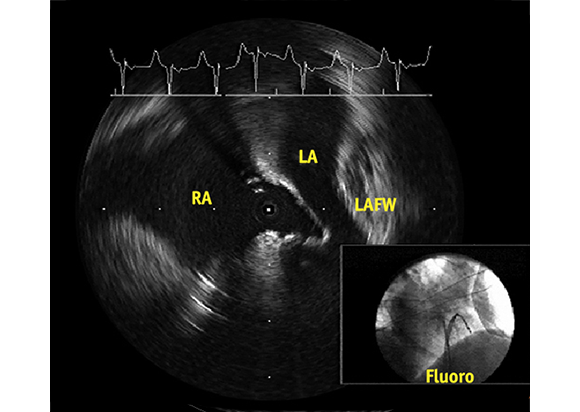
Crossing to the Septum to Help Guiding Left Sided Procedures
A key application for the ULTRA ICE PLUS catheter involves crossing the septum and then monitoring and helping to guide left-sided procedures. In this setting, ULTRA ICE PLUS catheter is designed to allow the user to:
- Visualize left atrial anatomy
- Confirm catheter location relative to the anatomy
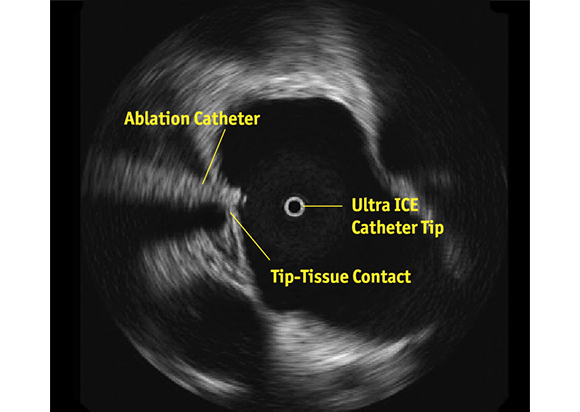
- Verify tip-to-tissue contact
- Identify location of the esophagus relative to the ablation catheter
- Characterize acute lesion morphology: swelling, dimpling, and crater formation
- Monitor for any early signs of thrombus formation, stenosis, or pericardial effusion
Product Specifications of ULTRA ICE PLUS Ultrasound Imaging Catheter
| Description | Specifications |
|---|---|
Shaft Diameter |
8.5 Fr |
Usable Length |
110 cm |
Imaging frequency |
9 MHz |
Ultrasound type |
Mechanically rotating transducer |
Distance from transducer to tip |
1.0 cm |
Image type |
Panoramic 360° view |
Imaging depth |
~6 cm radius (~12 cm diameter) |
Axial resolution |
≦ 0.29 mm |
Shaft rotation speed |
1800 RPM |
Frame refresh rate |
30 frame/sec |
Ultrasound pulse per full rotation |
256 |
Product Compatibility
| Imaging System | Catheter | Motor Drive Unit |
|---|---|---|
| POLARIS Multi-Modality Guidance System | ULTRA ICE™ PLUS | MDU5 PLUS |
| iLAB with POLARIS™ software | ULTRA ICE™ PLUS | MDU5 PLUS |
| iLAB with software version 2.7 or higher | ULTRA ICE™ PLUS | MDU5 PLUS |
Ordering Information
| Ref/Catalog Number | Description |
|---|---|
| M00499100 | ULTRA ICETM PLUS Ultrasound Imaging Catheter |